A
Smart Grid allows a bidirectional communication between buildings and monitor
units. In other words, the set of energy productors of any type and consumers
like devices, and the local electricity supply network are able to connect and
cooperate. Systems that optimize energy consumption and reclaim smart
technologies like Machine Learning, are used to balance ideally total energy
consumption and convenience.
There
is an opportunity of remote or in area control of the building functions using
smartphone applications. In order to work properly, a smart grid should obtain
the necessary hardware to take measurements of several environmental parameters
like temperature, light level or humidity.
Many applications have been spreading in the market. They usually are an implementation that reduces energy consumption using various automations, sensors and cutting-edge Machine Learning technologies. Such a system monitors everyday habits of the inhabitants and learns their schedule. Thus, it can customize the building’s conditions, adjust the lighting and almost every other type of devices, aiming at balancing between functionality and economy.

Such implementations include sensors and devices that establish a wireless connection with the processing unit of the building, which in many cases can be remotely located on the cloud. Anyway, it seems that modern communication protocols are required to enable data exchange. Technologies that are used in this field are wireless communication protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or 3G – 4G – 5G and they gradually lead to the next generation of “smart” devices that are supposed to replace the conventional ones.

When designing a near-Zero Energy Building, renewable energy sources are always of high significance. The aim is always eco-friendly societies. Options like solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy or biomass are common practises.
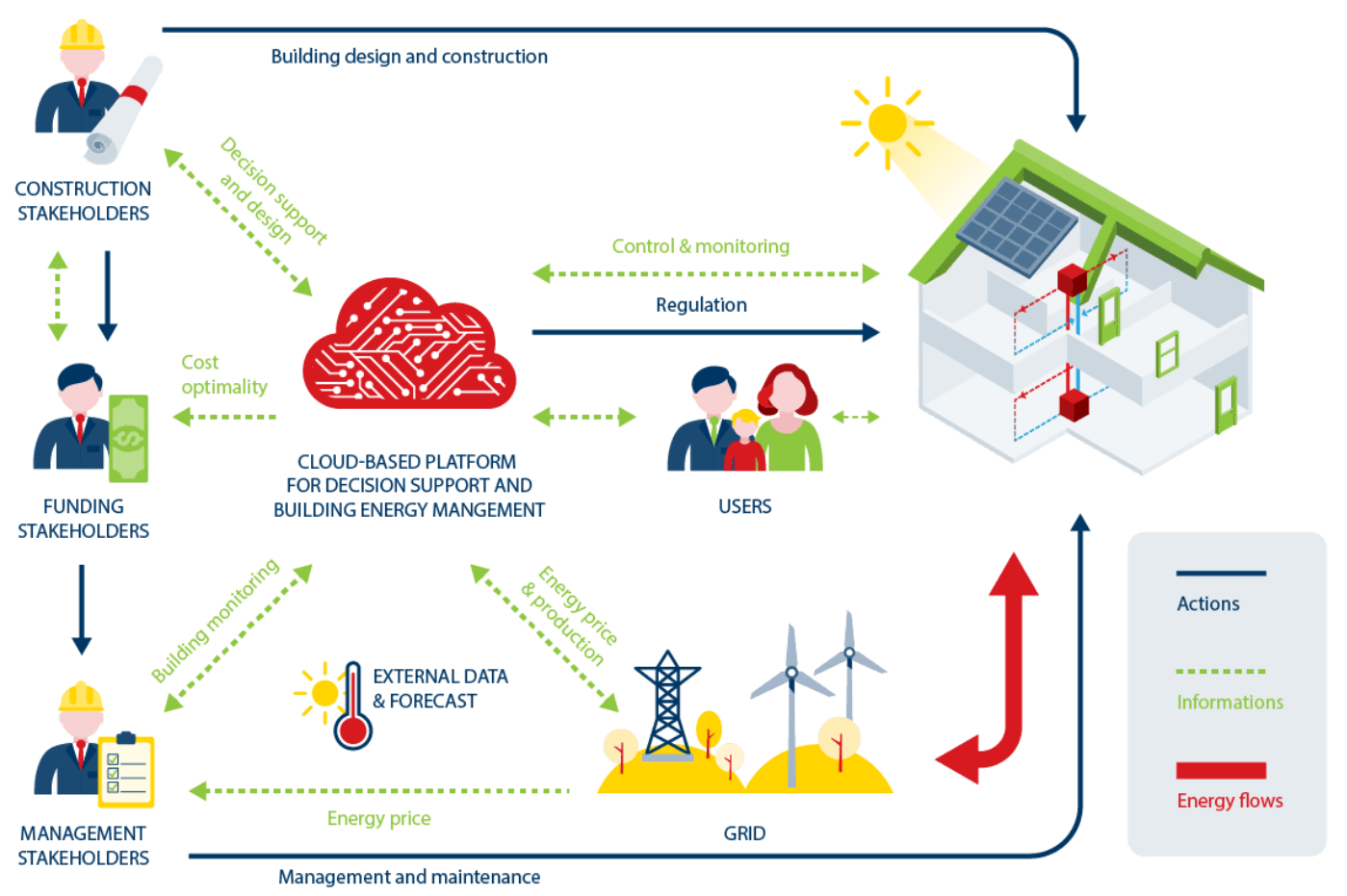
HEART is a project funded by the European Union that contracts energy upgrades of old constructions following the chart.
In areas with intense volcanic activity, structures that quarry heat from the ground can be the obvious solutions (geothermal energy). Heat that is produced in hydroelectric plants is also used when transported in the form of hot water in nearby towns and villages (district heating). It can be used for domestic use or underfloor heating. Apart from those, photovoltaic panels and solar heaters utilize solar potential for domestic needs making good use of the photoelectric effect. In addition, heat pumps work like refrigerators in reverse, as they derive heat from the environment and channel it into the building. As far as eco-friendly function is concerned, devices that use a thermostat, like air conditioners or refrigerators, can result in lower electricity consumptions.
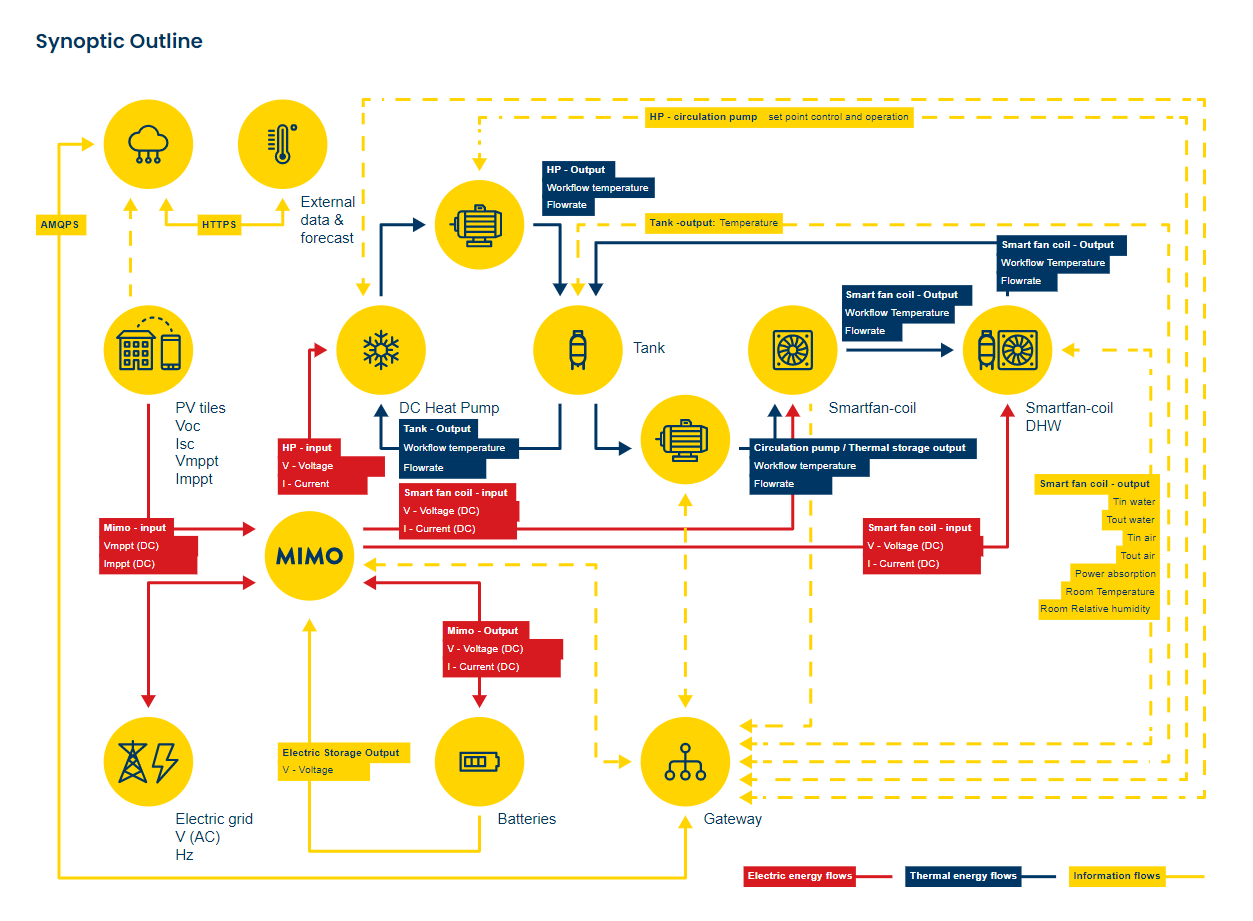
HEART’s monitoring system optimizes building’s total energy performance and enables cooperation between components like devices, PV panels, batteries, solar heaters, heat pumps, lights, sensors, external data from cloud and local energy supply network.

Another
issue is construction. It’s important to install proper insulation and use materials
with low heat permeability. In Greece 6 out of 10 buildings are made without
original insulation at all, thus an energy upgrade could save much energy for
the owners. A combination of airtightness, in other words the control of air
leakage, and triple glazed glass windows can also improve the inside environment.
In addition, a lighting automation system that uses light and motion sensors
can also help saving electricity, ideally combined with eco-friendly light
bulbs.
created with
Joomla Page Builder .